

Nemo Projecteur 365 Wall Ceiling Light Le Corbusier Outdoor
- Regular price
- £800.00
- Sale price
- £800.00
- Regular price
-
Special order or made to order items
Orders placed for items that are not in stock in our warehouse are advertised as "Delivery within XXX".
Upon purchase, orders are placed with our suppliers, which are then delivered to our warehouse whereby they are then shipped directly to you within 24 business hours.
The delivery time advertised is a generous timeframe, and most items are received within this period.
However, this not guaranteed as we rely on production schediules and supply chains and quite often internail customs.
Don't Panik - Shop with confidence
- 5 star feefo reviews
- Established 2001
- UK largest independant stockist
- UK customer support
- UK next working day delivery avaliable on ALL in stock items
- Secure payments
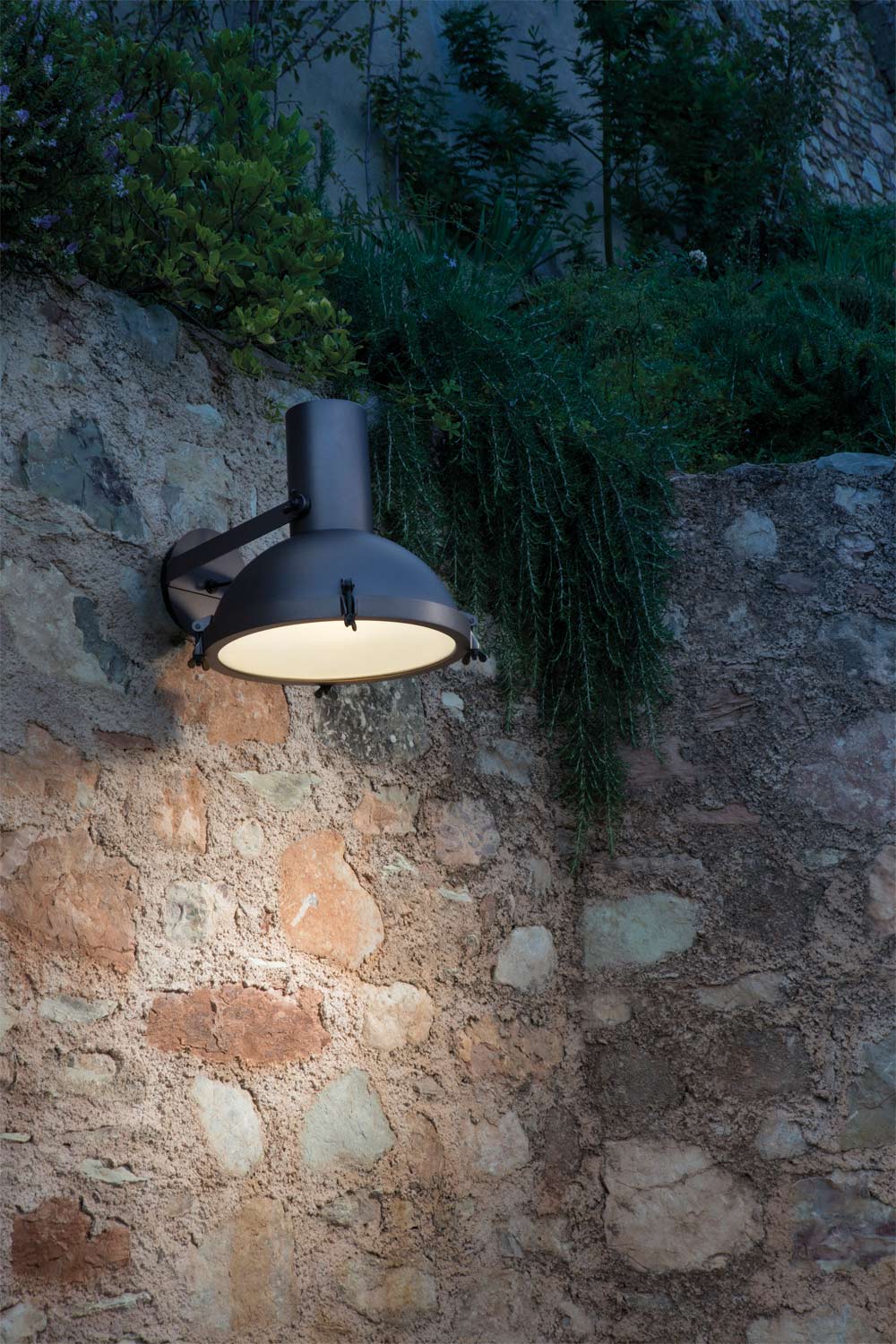
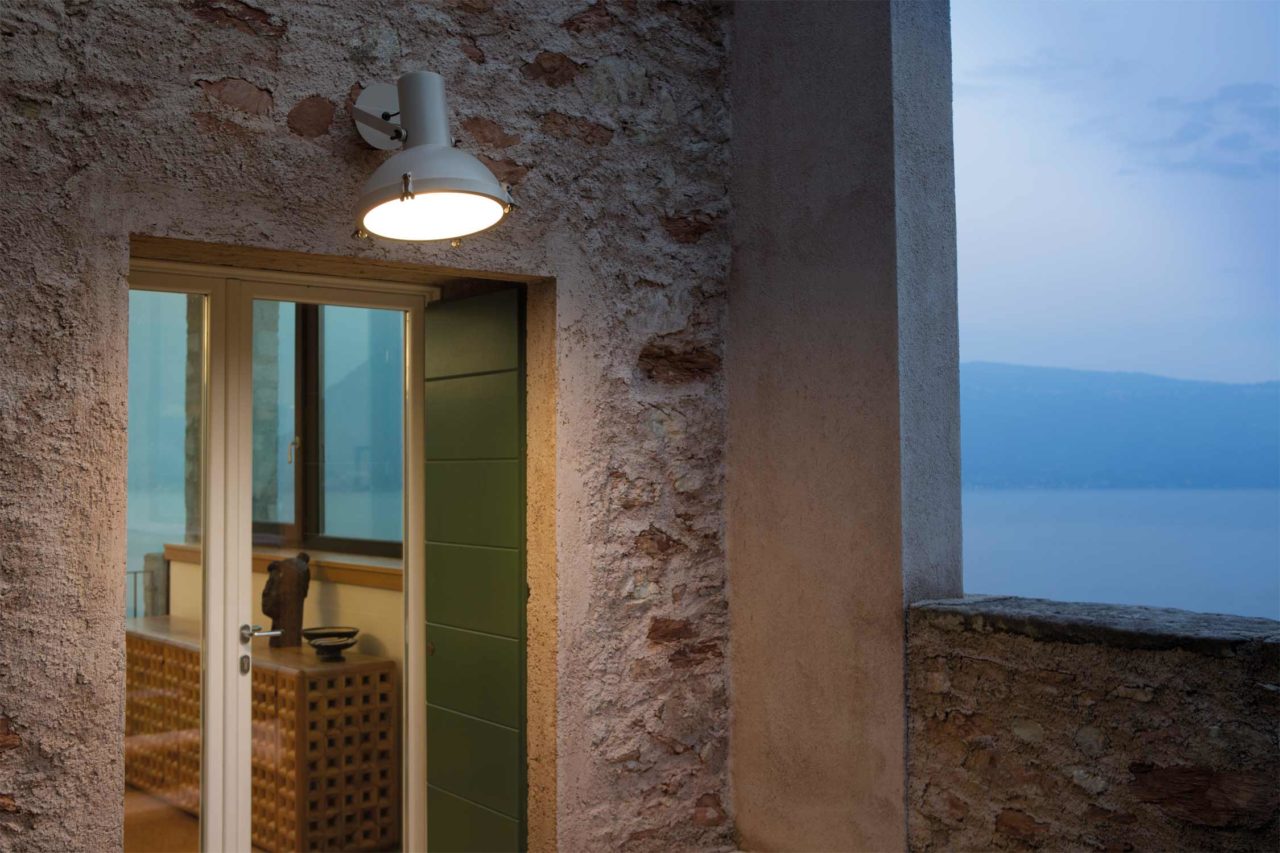
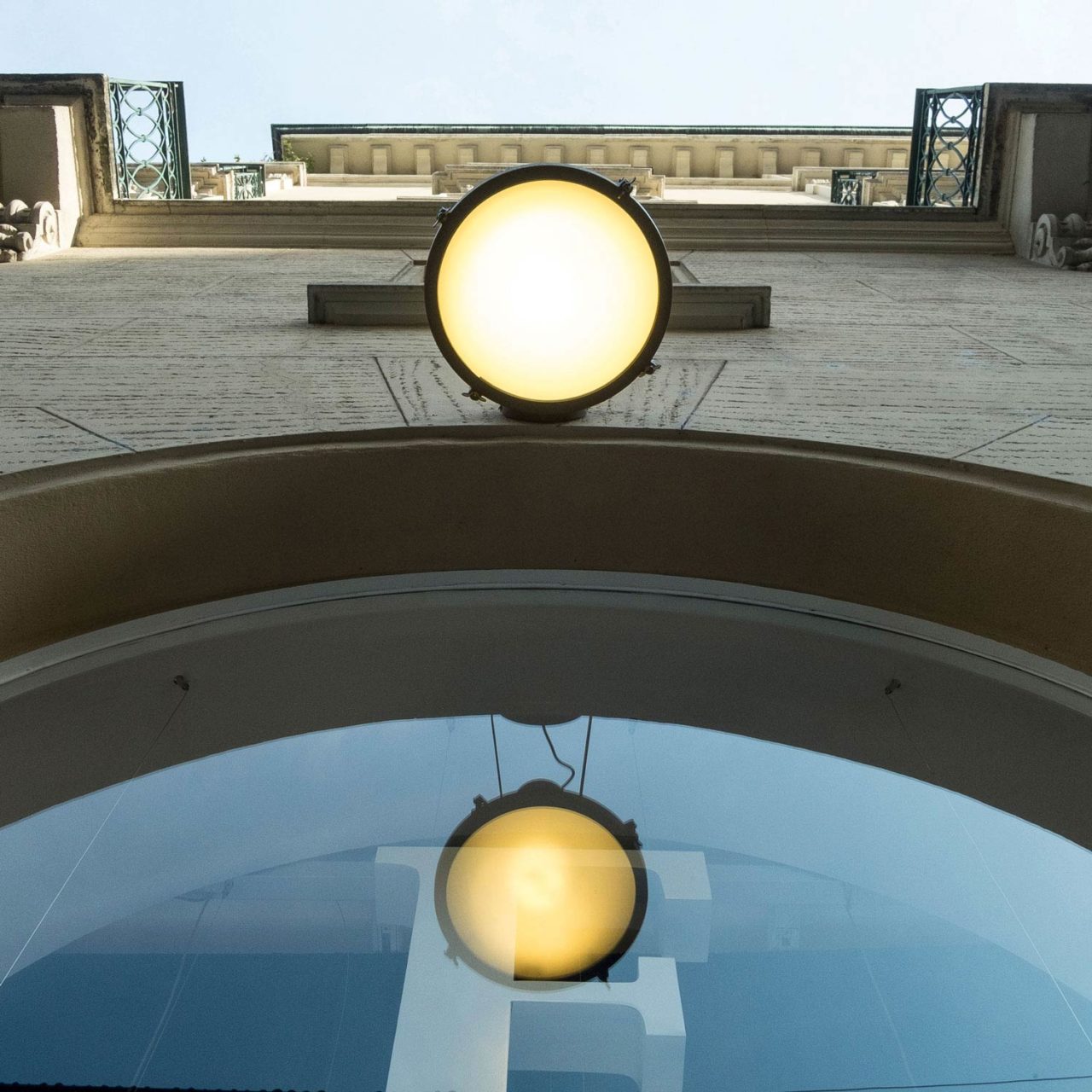
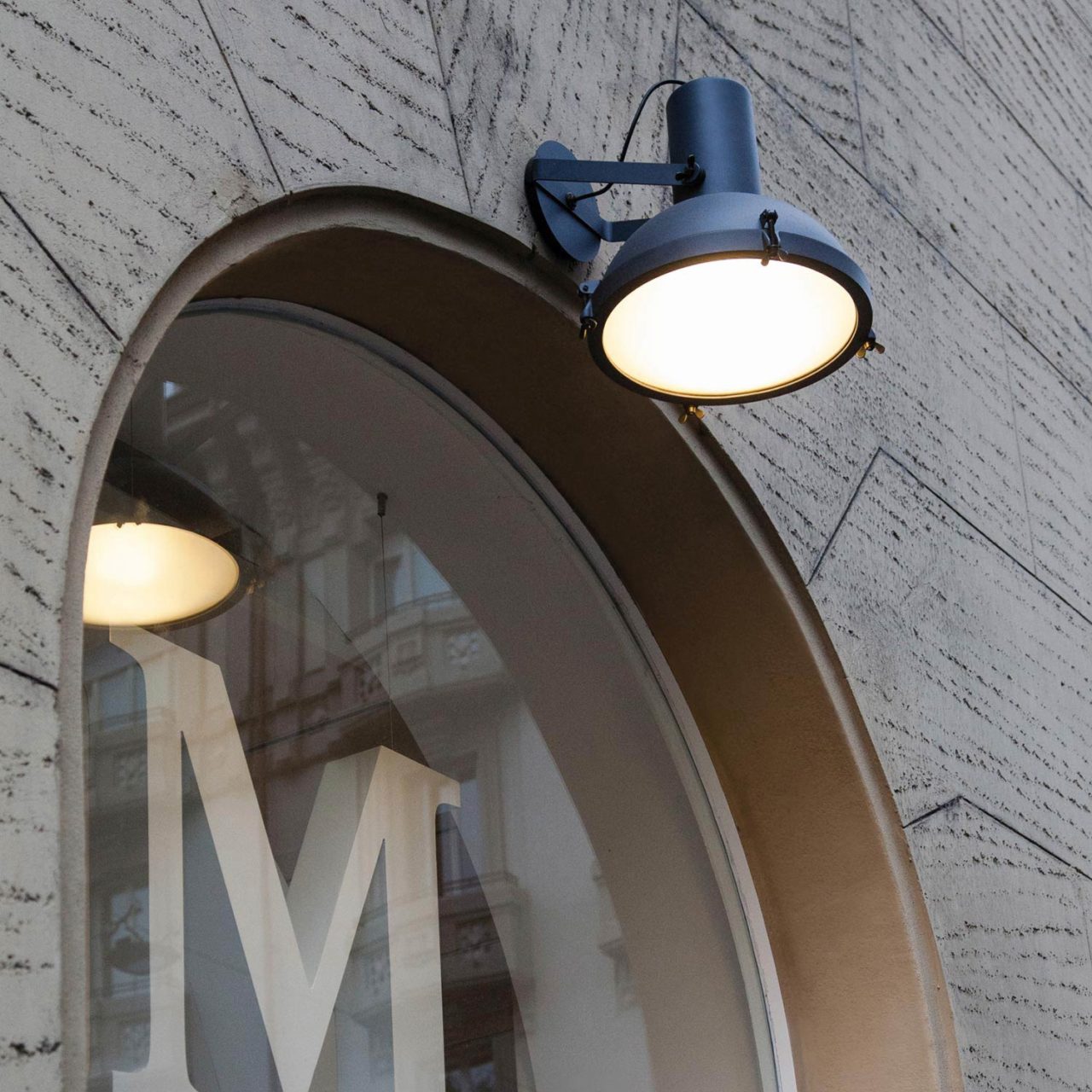
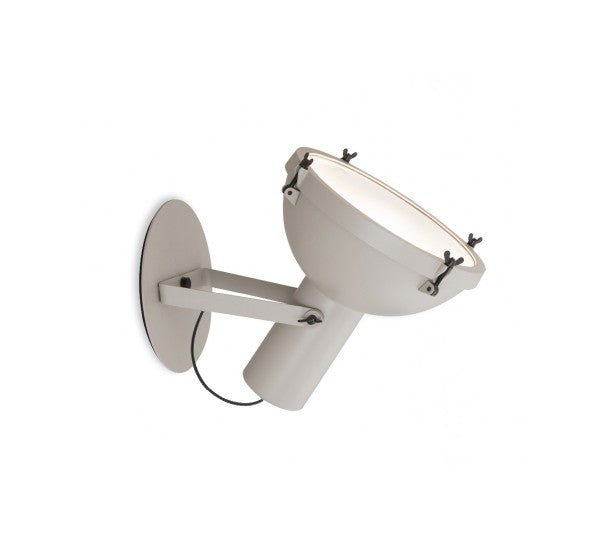
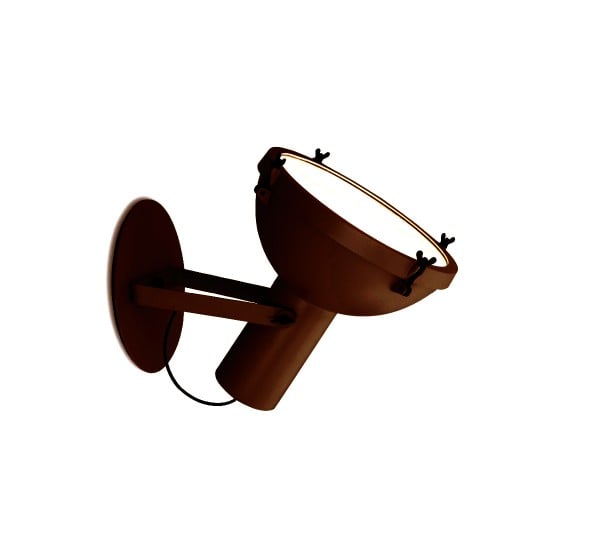
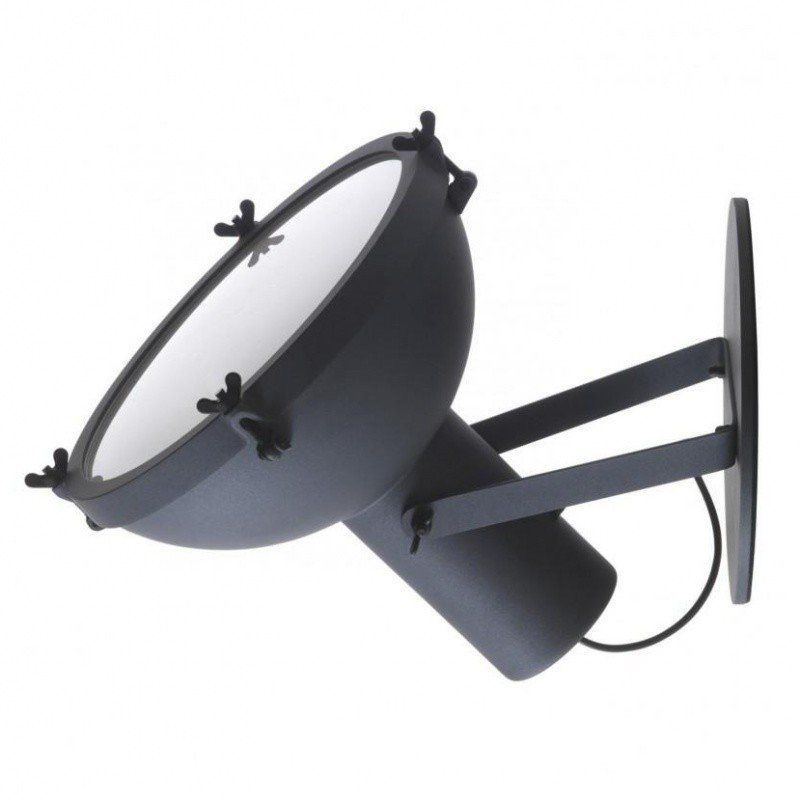
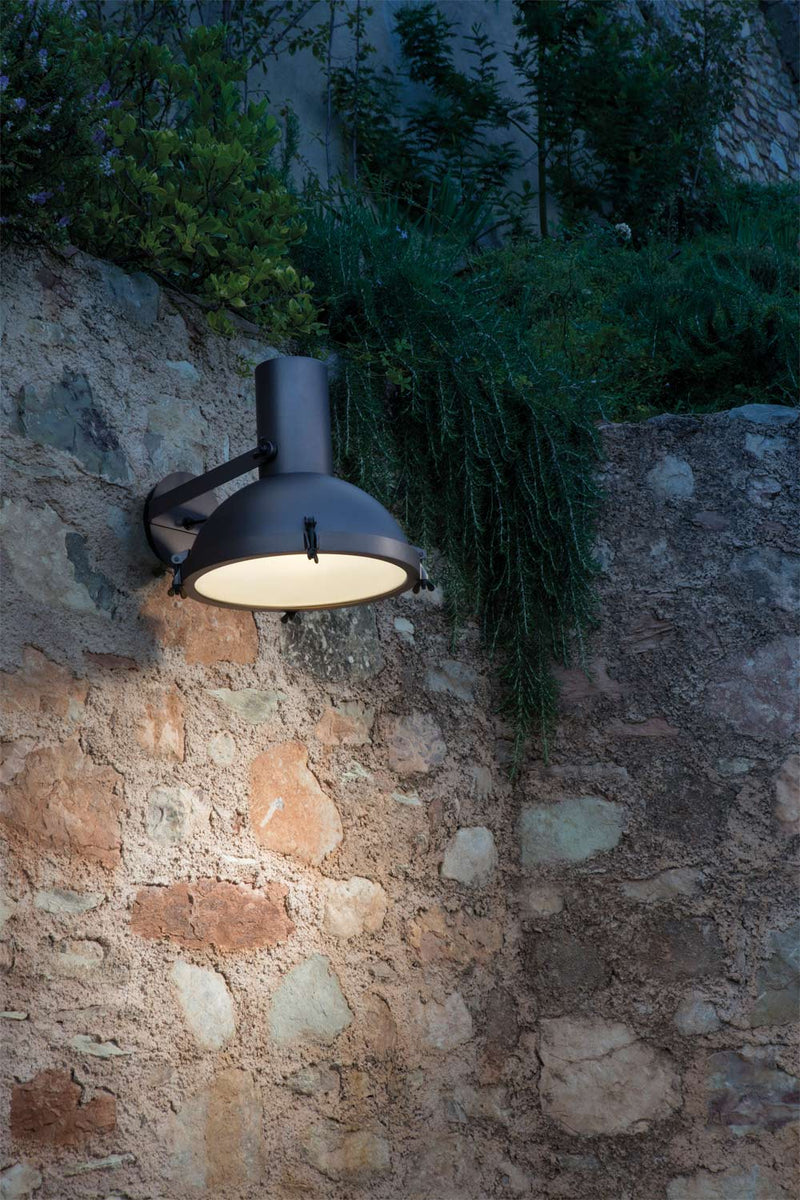
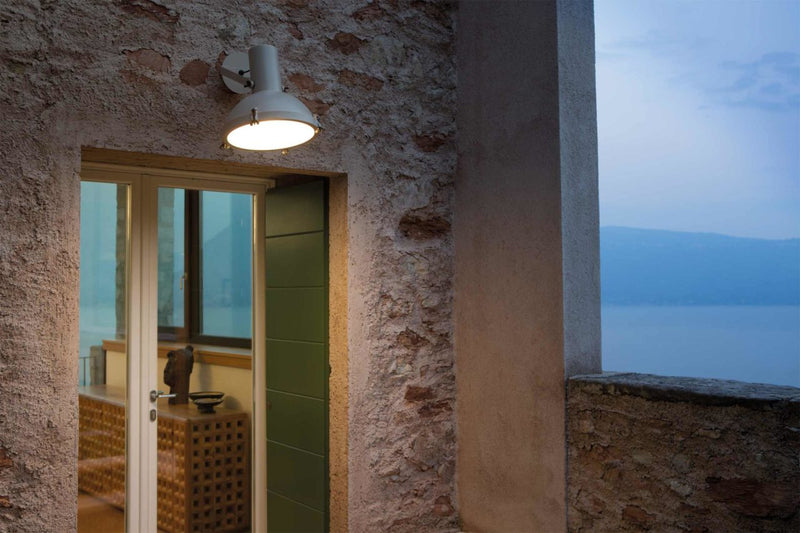
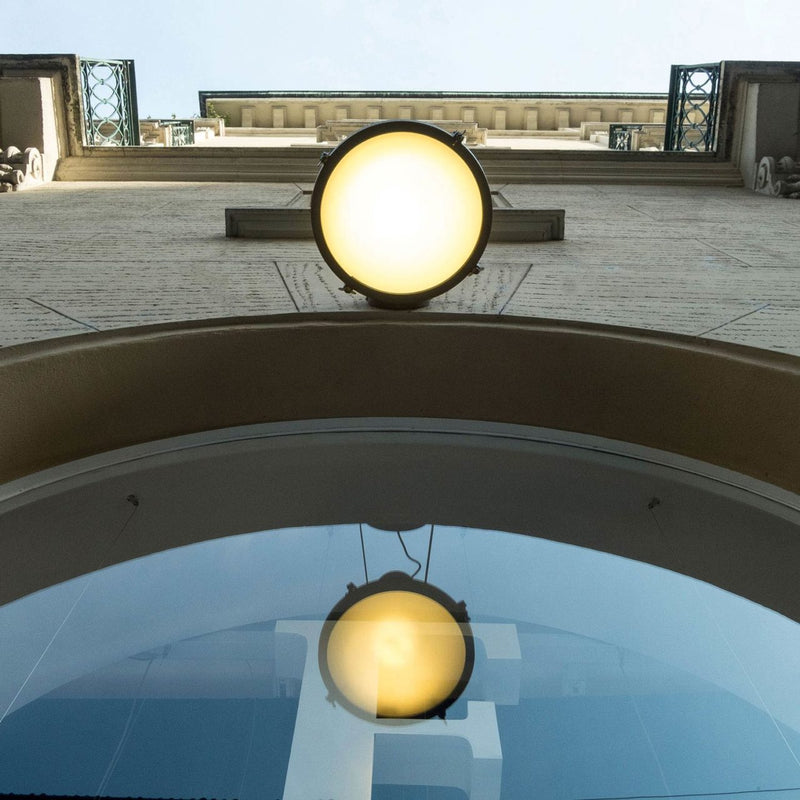
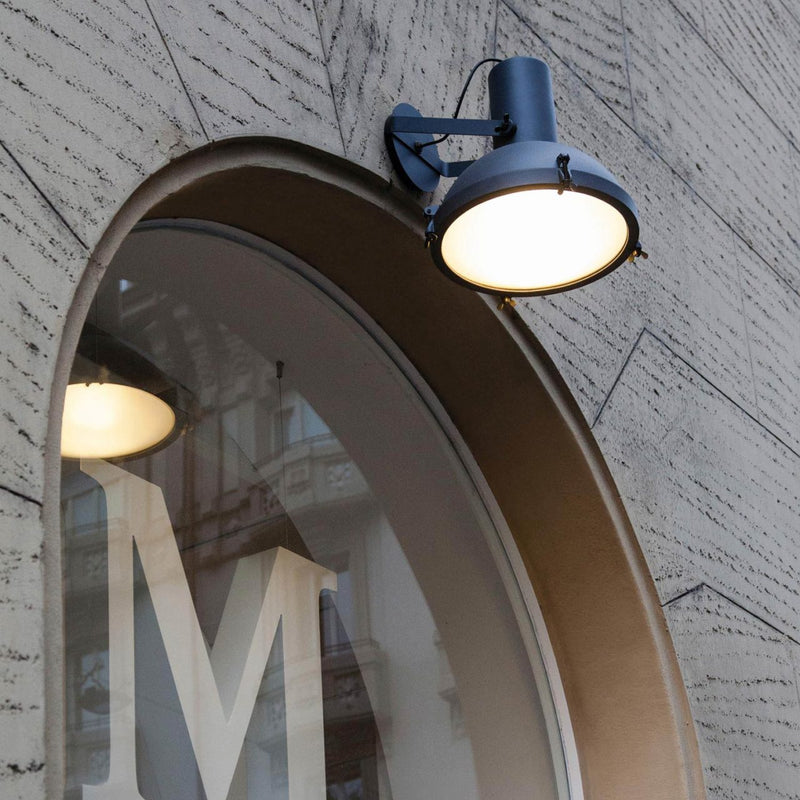
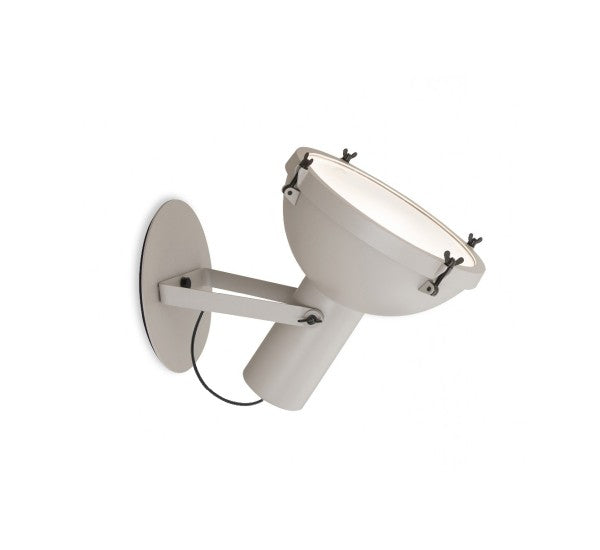
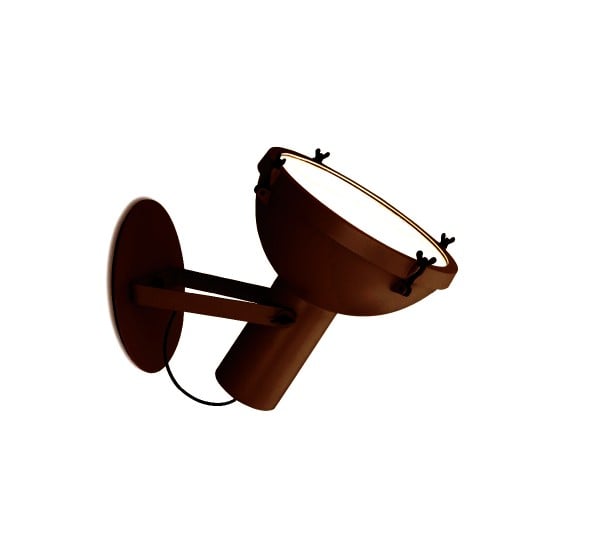
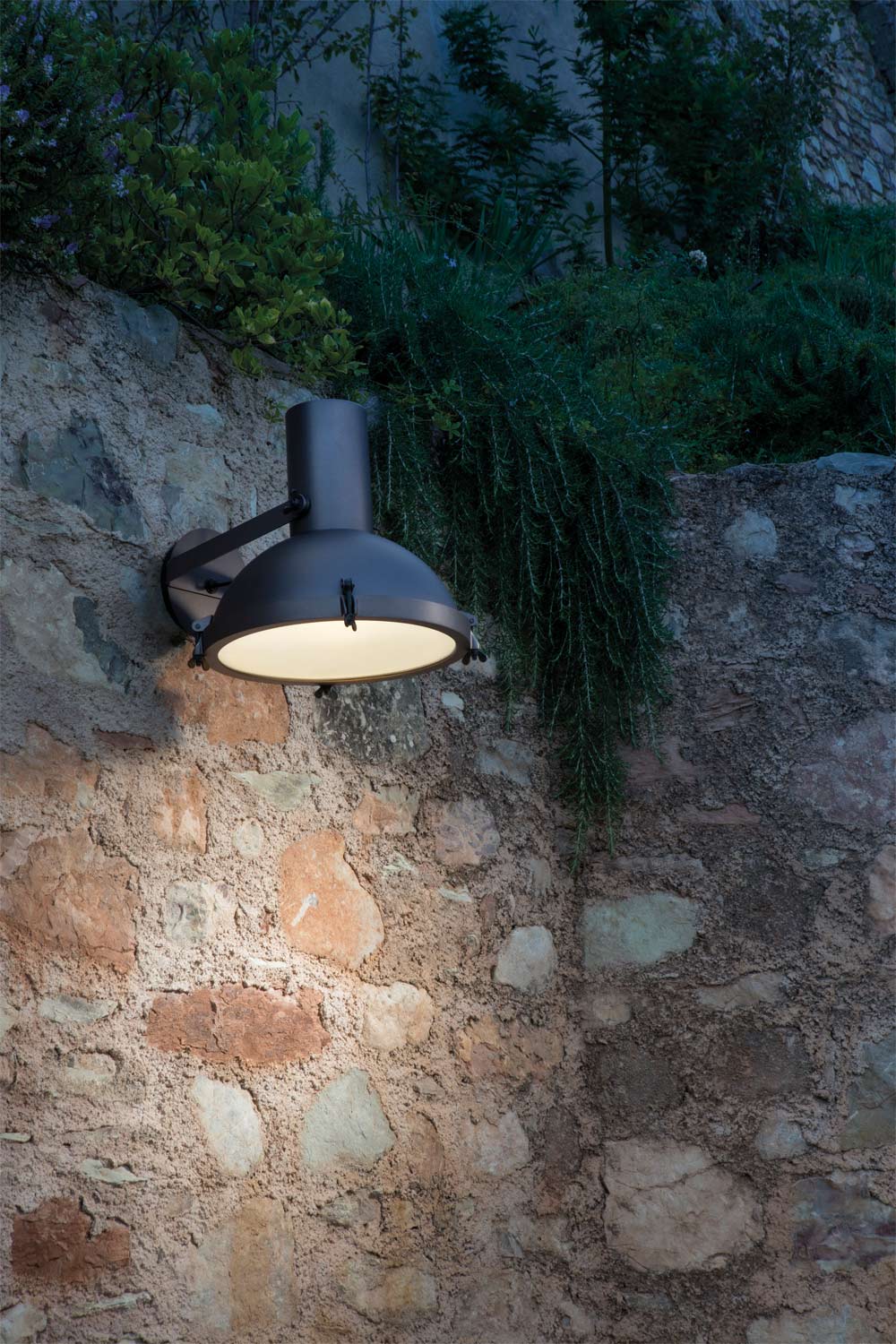
Nemo Projecteur 365 Wall Ceiling Light Le Corbusier Outdoor
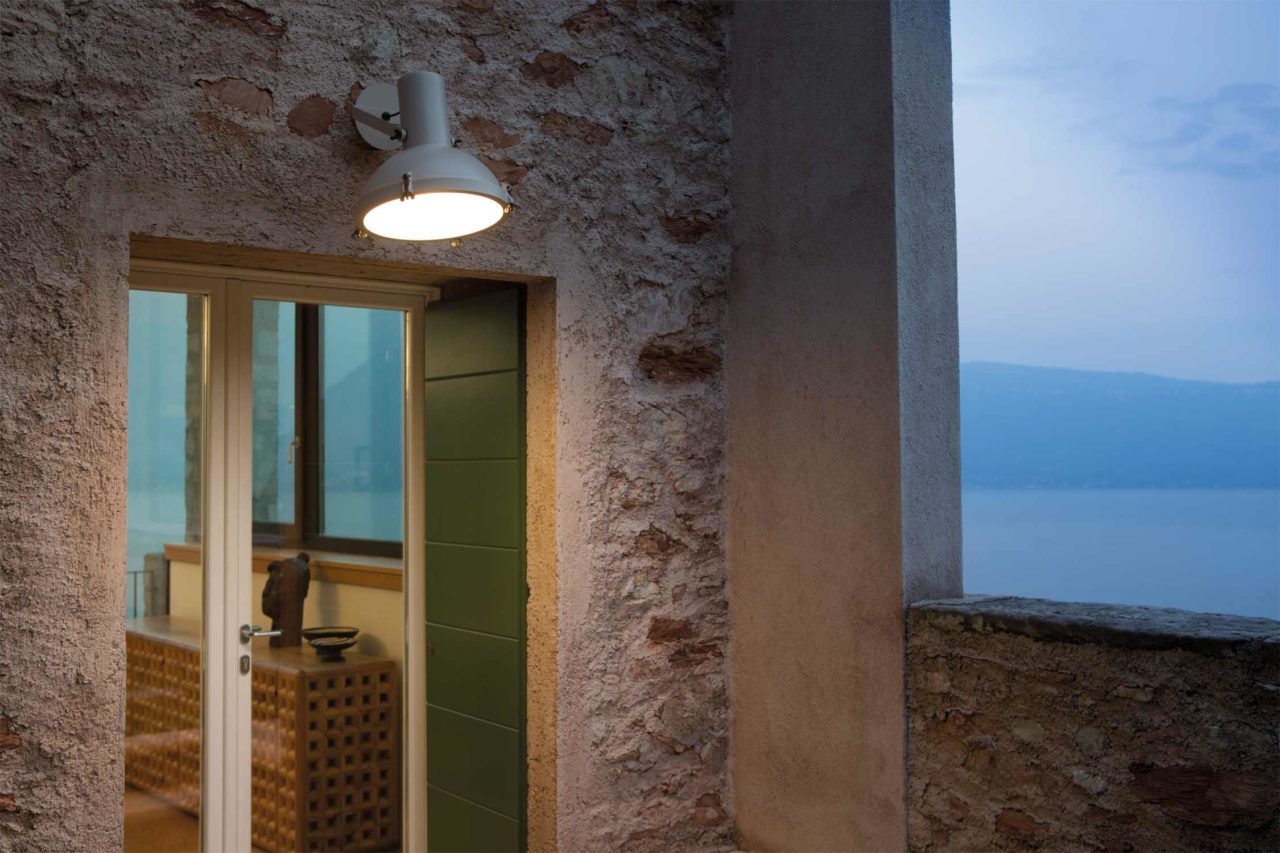
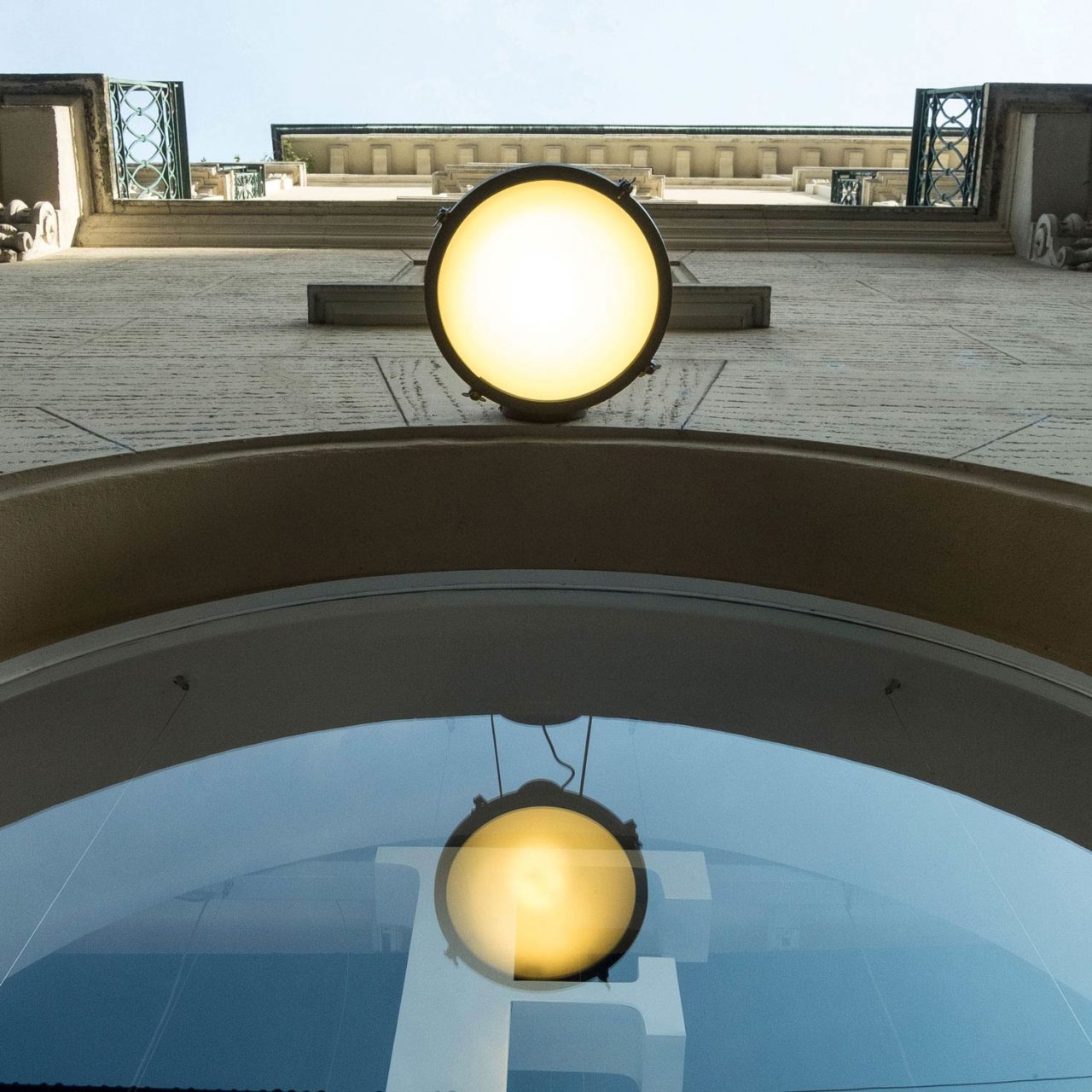
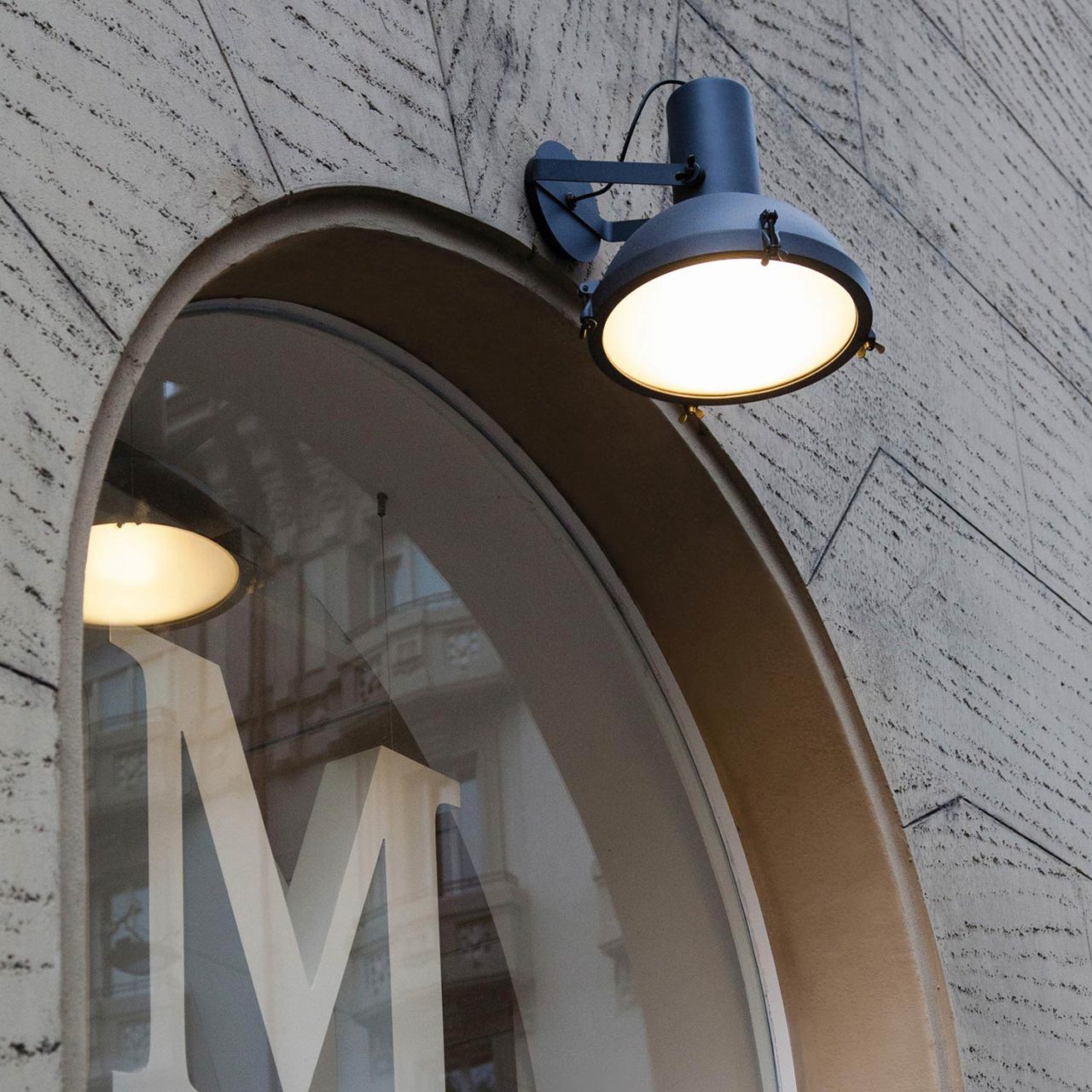
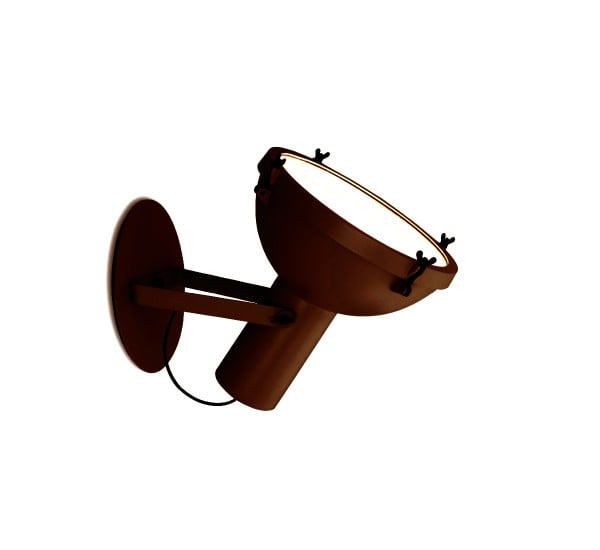
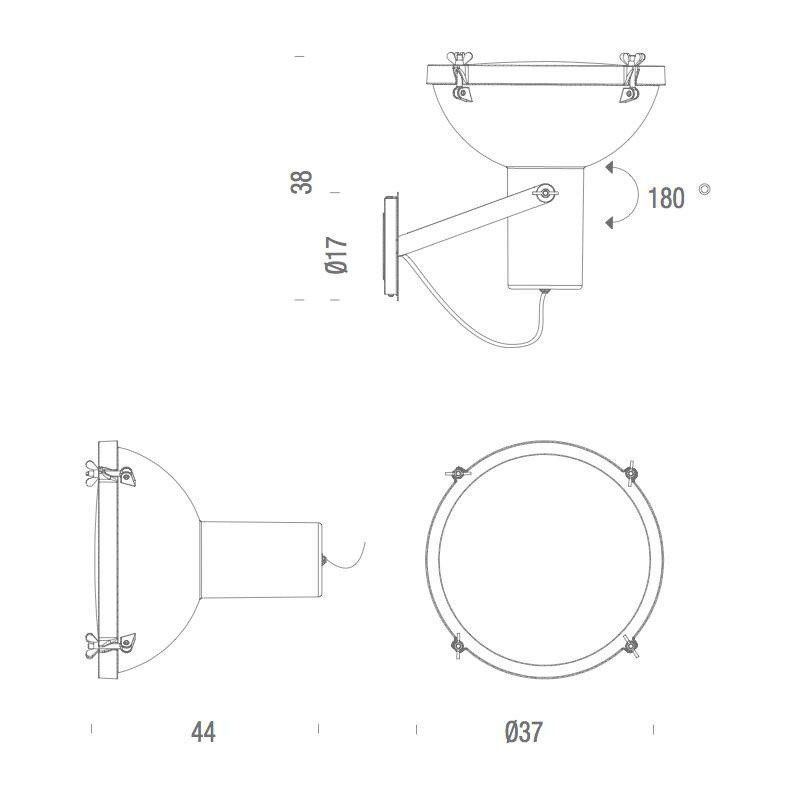
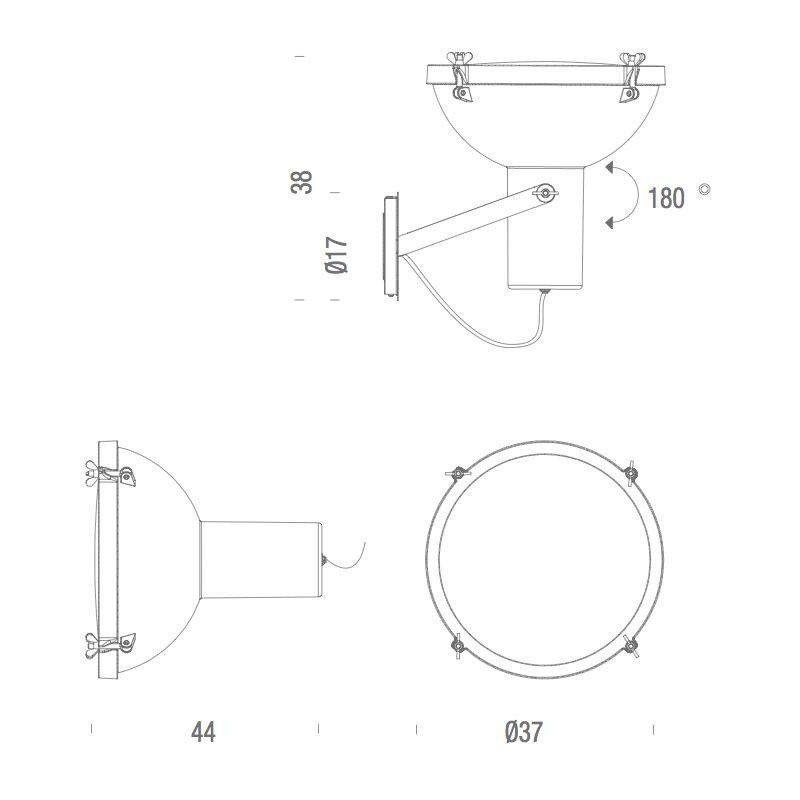
The Projecteur by Le Corbusier was designed for the Chandigarh High Court, India, in 1954. Aluminium body painted in night blue, white sand or moka. Diffuser glass curved and sandblasted in the inner part. Painted canopy, screws and small metal parts black chromed.
Outdoor version (IP54).
Bulb: 1x 60W E27 (not included)
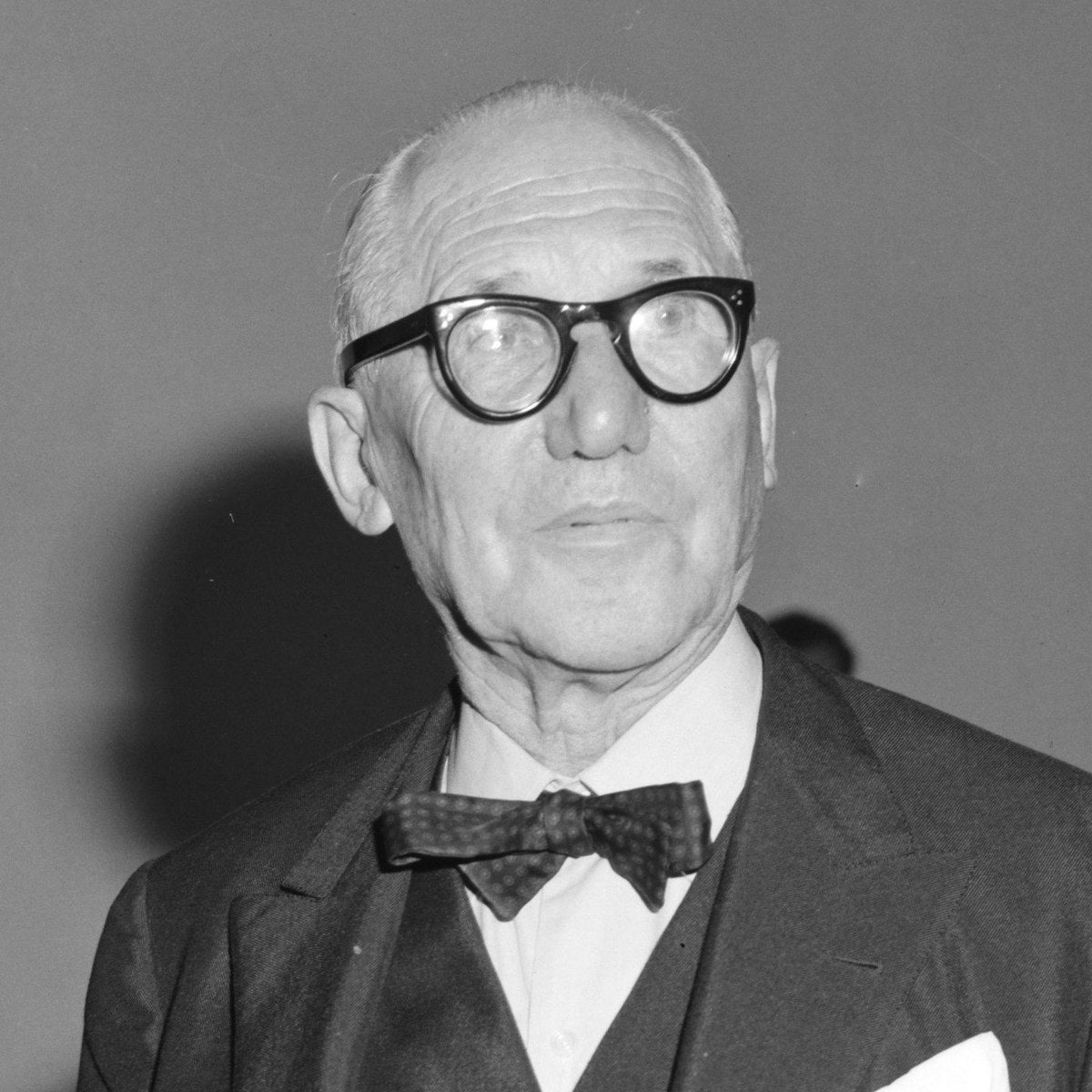
LE CORBUSIER
“Our eyes are made to see forms in light; light and shade reveal these forms; cubes, cones, spheres, cylinders or pyramids are the great primary forms which light reveals to advantage; the image of these is distinct and tangible within us without ambiguity. It is for this reason that these are beautiful forms, the most beautiful forms”.

Le Corbusier
LE CORBUSIER, born Charles-Edouard Jeanneret-Gris in 1887 in Switzerland, was an architect, designer, urbanist, and writer, famous for being one of the pioneers of what is now called modern architecture. His career spanned five decades, with his buildings constructed throughout Europe, India, Japan and America. He was a pioneer in studies of modern high design and was dedicated to providing better living conditions for the residents of crowded cities. In 1918, Le Corbusier met the Cubist painter Amédée Ozenfant. Rejecting Cubism as irrational and "romantic", the pair jointly published their manifesto, 'Après le cubisme' and established a new artistic movement, Purism. They established the Purist journal 'L'Esprit nouveau'. It was Le Corbusier's Villa Savoye (1929–1931) that most succinctly summed up his five points of architecture that he had elucidated in 'L'Esprit Nouveau' and his book 'Vers une architecture'. By 1927, Le Corbusier was among the world's leading practitioners of the New Architecture. He collaborated with Charlotte Perriand on furniture – including the LC4 – which is still an icon of modern design. Around 1942, he formulated his "Modulor" theory to facilitate architecture on a human scale. In the 1950s, an opportunity to translate the Radiant City on a large scale occurred in the construction of the Union Territory Chandigarh and the first planned city in India. In 1952, the first 'Unité d'Habitation' was completed in Marseille, followed by further modular residential units and the pilgrimage chapel at Ronchamps in 1955 – He died in 1965 in Roquebrune-Cap-Martin, France.